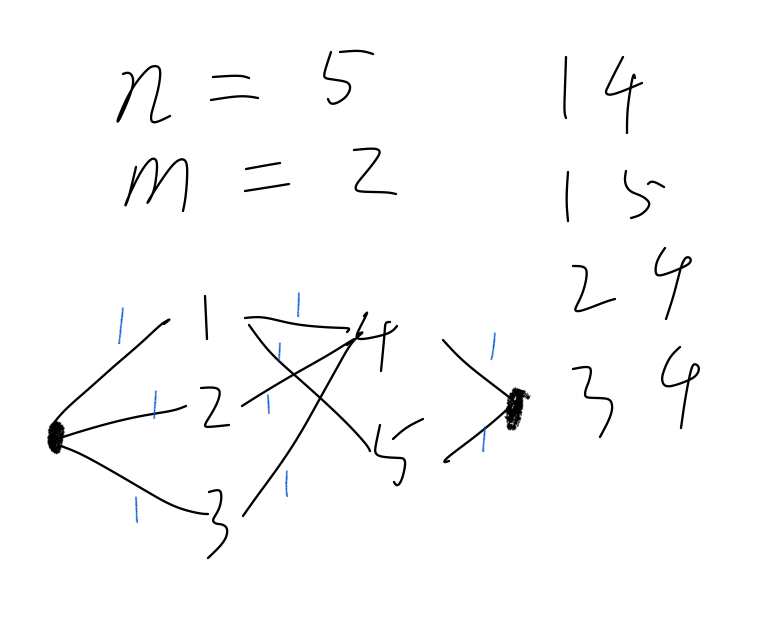
如图,可以看作从源点流向正驾驶员,再流向副驾驶员,最后流向汇点,每条边流量均为1
Code
1/**
2 * author: Akvicor
3 * created: 2019-07-26 18-37-11
4**/
5
6#include <bits/stdc++.h>
7
8using namespace std;
9
10#ifdef DEBUG
11#define FAST_IO 17
12#else
13#define FAST_IO //ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0)
14#define endl '\n'
15#endif
16
17#define rep(i, n) for(int i = 0; i < (n); ++i)
18#define reep(i, n) for(int i = 0; i <= (n); ++i)
19#define lop(i, a, n) for(int i = a; i < (n); ++i)
20#define loop(i, a, n) for(int i = a; i <= (n); ++i)
21#define per(i, a, n) for(int i = a; i >= n; --i)
22#define prec(x) fixed << setprecision(x)
23#define ms(s, n) memset(s, n, sizeof(s))
24#define mod(x) ((x) %= MOD)
25#define all(v) (v).begin(), (v).end()
26#define sz(x) ((int)(x).size())
27#define mp(x, y) make_pair(x, y)
28#define pb(x) push_back(x)
29#define fi first
30#define se second
31#define MOD(x) const int MOD = (int)x
32#define MAXN(x) const int MAXN = (int)x + 10
33
34typedef long long LL;
35typedef unsigned long long ULL;
36typedef pair<int, int> PII;
37typedef vector<int> VI;
38typedef vector<PII> VII;
39typedef pair<LL, LL> PLL;
40typedef vector<LL> VL;
41typedef vector<PLL> VLL;
42
43namespace SOL {
44
45 const double EPS = 1e-6;
46 const double PI = acos(-1.0);
47 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
48 const LL LINF = 0x7f7f7f7f7f7f7f7f;
49
50/** >------- Akvicor's Solution -------< **/
51
52 MOD(1e9 + 7);
53 MAXN(5e3);
54
55 struct Dinic {
56 Dinic(int n) {
57 G = vector<vector<int> >(n + 10);
58 d = vector<int>(n + 10);
59 vis = vector<bool>(n + 10);
60 cur = vector<int>(n + 10);
61 }
62
63 struct Edge {
64 int from, to, cap, flow;
65 };
66
67 int s, t; //节点数,边数,源点编号,汇点编号
68 vector<Edge> edges; //边表,edges[e]和edges[e^1]互为反向弧
69 vector<vector<int> > G; //邻接表,G[i][j]表示节点i的第j条边在e中的序号
70 vector<bool> vis; //bfs用
71 vector<int> d; //从起点到i的距离
72 vector<int> cur; //当前弧下标
73 void add_edge(int from, int to, int cap) {
74 edges.push_back({from, to, cap, 0});
75 edges.push_back({to, from, 0, 0});
76 G[from].push_back(edges.size() - 2);
77 G[to].push_back(edges.size() - 1);
78 }
79
80 bool BFS() {
81 fill(vis.begin(), vis.end(), false);
82 queue<int> q;
83 q.push(s);
84 d[s] = 0;
85 vis[s] = true;
86 while (!q.empty()) {
87 for (int id : G[q.front()]) {
88 Edge &e = edges[id];
89 if (!vis[e.to] && e.cap > e.flow) {
90 vis[e.to] = true;
91 d[e.to] = d[q.front()] + 1;
92 q.push(e.to);
93 }
94 }
95 q.pop();
96 }
97 return vis[t];
98 }
99
100 long long DFS(int u, int a) {
101 if (u == t || a == 0) return a;
102 int flow = 0, f;
103 for (int &i = cur[u]; i < (int) G[u].size(); ++i) {
104 Edge &e = edges[G[u][i]];
105 if (d[u] + 1 == d[e.to] &&
106 (f = DFS(e.to, min(a, e.cap - e.flow))) > 0) {
107 e.flow += f;
108 edges[G[u][i] ^ 1].flow -= f;
109 flow += f;
110 a -= f;
111 if (a == 0) break;
112 }
113 }
114 return flow;
115 }
116
117 long long run(int _s, int _t) {
118 s = _s;
119 t = _t;
120 long long flow = 0;
121 while (BFS()) {
122 fill(cur.begin(), cur.end(), 0);
123 flow += DFS(s, 0x3f3f3f3f);
124 }
125 return flow;
126 }
127 };
128
129 void solve() {
130 FAST_IO;
131
132 int n, m, u, v, w;
133
134 cin >> n >> m;
135 struct Dinic di = Dinic(n);
136
137 for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i){
138 di.add_edge(0, i, 1);
139 }
140 for(int i = m+1; i <= n; ++i){
141 di.add_edge(i, n+1, 1);
142 }
143 while(cin >> u >> v){
144 di.add_edge(u, v, 1);
145 }
146 cout << di.run(0, n+1) << endl;
147 }
148
149/** >----------------------------------< **/
150
151}
152
153int main() {
154
155#ifdef DEBUG
156 int DEBUGCNT = 0;
157 clock_t DEBUGstart, DEBUGfinish;
158 double DEBUGduration;
159 cout << endl << ">------- Akvicor's Solution -------<" << endl << endl;
160 while (DEBUGCNT < 70) {
161 cout << ">---> Test: #" << DEBUGCNT << " <---<" << endl;
162 DEBUGstart = clock();
163#endif
164
165 SOL::solve();
166
167#ifdef DEBUG
168 DEBUGfinish = clock();
169 DEBUGduration = (double)(DEBUGfinish - DEBUGstart)*1000 / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
170 cout << ">---> Test: #" << DEBUGCNT << " time: " << fixed << setprecision(4) << DEBUGduration << " ms <---<" << endl << endl;
171 if (cin.eof()) break;
172 if (!cin.good()) break;
173 if (cin.fail()) break;
174 if (cin.bad()) break;
175 ++DEBUGCNT;
176 }
177 cout << ">----------------------------------<" << endl << endl;
178#endif
179
180 return 0;
181}
除另有声明外,本博客文章均采用 知识共享 (Creative Commons) 署名 4.0 国际许可协议 进行许可。转载请注明原作者与文章出处。